what is plastic mold
Published: Jul 2018 · Last updated: Jan 2026
This guide is reviewed periodically using recent tooling + production quote data.
What is a plastic mold? A plastic mold is a precision tool used to mold molten plastic into uniform components, primarily in mass plastic production. Plastic molds are among the most crucial tools in modern production. And they would transform complex designs into repeatable products with strict tolerances and good performance. These tools can be used to produce mass plastic production for automotive interiors, medical disposables, and consumer electronics housings.
We are professional plastic mold manufacturers with 18 years of experience, and we can combine the choice of steel, cooling design, gating, and process control to enhance quality, shorter cycle time, and lower unit cost. This guide describes plastic mold, the injection molding process, plastic materials, cost, injection molding problems, and industry trends to select the correct plastic solutions.
Learning the Basics of Plastic Molds
It is useful to come to an agreement on definitions and structure before settling on a tool. The mechanism and major components of the mold have been briefly summarized below.
Definition and Major Components
A plastic mold is a special device that applies injection, blow, compression, transfer, and rotational types of molding to provide thermoplastic or thermoset materials with the final geometry. In the centre lies the cavity (negative of the external shape) and core (creating internal features). Liquid plastic is injected through a system of injection, cooling, solidification, and ejection consistently, which is a full injection molding cycle. Standard steels are P20, H13, and S136 stainless, and prototypes are made of CNC machining,3d printing, and vacuum casting.
Injection molding process: plastic is melted and injected or pressed into the mold cavity under constant pressure from the press, and hardens during cooling. The part is ejected after the mold opens, and the cycle is repeated. The quality of parts is based on plastic material, steel, geometry, gating, cooling layout, and ejection way.
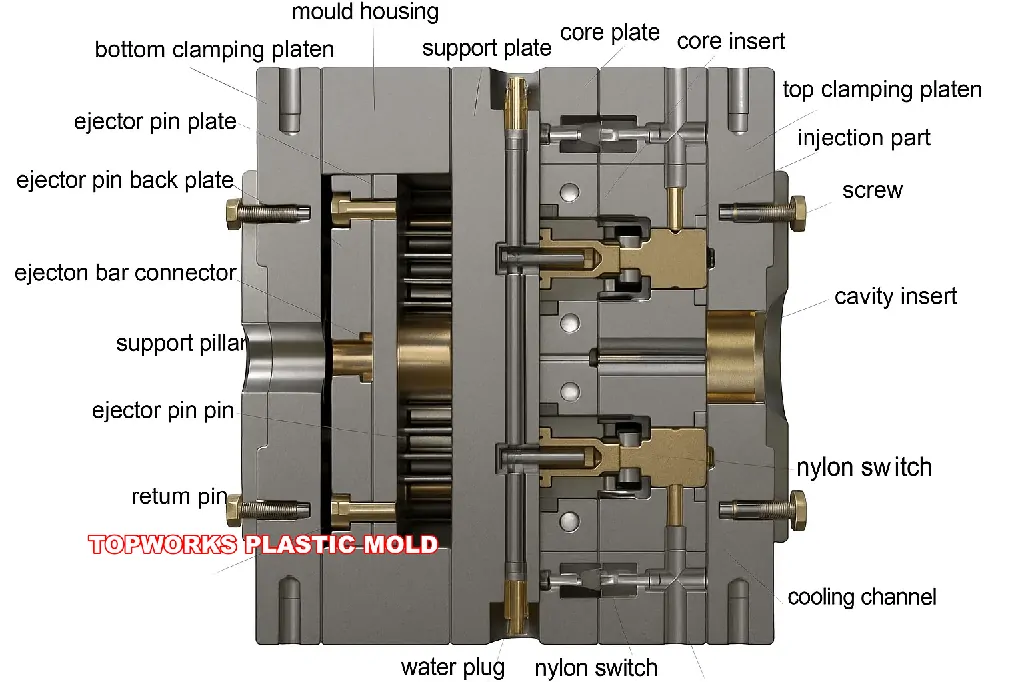
| Component | Primary Function | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cavity | Defines exterior geometry and cosmetic surfaces. | Controls appearance grade, surface finish, and texture applied here. |
| Core | Forms internal geometry (bosses, ribs, holes). | Critical for structural features and dimensional stability. |
| Cooling System | Manages cycle time and dimensional stability. | Water lines, baffles, or conformal channels optimize heat removal. |
| Ejection System | Safely releases the part from the mold with good quality | Ejector pins, sleeves, lifters, and air valves; timing and placement matter. |
| Runner System | Delivers melt evenly to each cavity. Hot runner and cold runner system | Includes sprue, runners, and gates; balance flow to avoid defects.2 or 3 plates mold |
Related reading: Our Mold Manufacturing Services
Types of Plastic Molds
| Type of Mold | What it is | How it works | Best for | Advantages | Typical Cost | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molds | Bottles, containers, jerrycans, cosmetic, and pharma packaging. | Plasticizing → Injection fill → Pack/hold → Cooling → Mold open → Ejection → Repeat. | High-precision functional parts and cosmetic housings (connectors, dashboards, consumer electronics). | High accuracy and repeatability; short cycles at high volumes; supports intricate details. | $3,000–$100,000 | 4–10 weeks |
| Blow Molds | A mold for forming hollow parts. | Parison or preform → Clamp mold → Inflate to conform → Cool → Eject. | Bottles, containers, jerrycans, cosmetic and pharma packaging. | One-step hollow forming; lightweight parts; high material efficiency. | $3,000–$50,000 | 3–6 weeks |
| Compression Molds | A mold for compression forming, often for thermosets or sheet materials. | Place charge → Close and heat/press → Cure → Open and eject. | Large panels, insulators, composite components. | Low shear and internal stress; suited to thick sections and thermosets. | $5,000–$60,000 | 4–10 weeks |
| Transfer Molds | A mold that transfers heated material into cavities—great for parts with inserts. | Preheated charge in a pot → Pressurize → Flow to cavities → Cure → Eject. | Electrical parts with metal inserts, coil bobbins. | Accurate insert positioning; supports fine features and complex geometry. | $8,000–$80,000 | 5–10 weeks |
| Rotational Molds | A mold used in rotomolding for large hollow products. | Load powder → Heat while bi-axially rotating → Uniform coating → Cool → Demold. | Tanks, kayaks, large bins. | Very large seamless hollow parts; uniform wall thickness; low internal stress. | $3,000–$40,000 | 3–8 weeks |
How Does Plastic Molding Work?
Here’s the complete workflow, with injection molding as the anchor example. The same logic applies broadly across other molding methods.
The Complete Process (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Design Phase(Timeline: 1 weeks)
- CAD design: Part and mold 3D/2D, GD&T, draft, and tolerances.
- DFM analysis: Wall thickness, ribs, radii to reduce warpage and sink.
- Moldflow analysis: Filling balance, weld lines, air traps, cooling, and deflection prediction.
Step 2: Mold Fabrication(Timeline: 2–6 weeks)
- Material selection: P20, H13, S136, or aluminum based on life, resin, and corrosion risk.
- CNC machining: Rough/finish for geometry accuracy; electrodes for EDM.
- EDM machining: Deep pockets, sharp corners, complex details.
- Polishing & texturing: Optical polish (SPI A1/A2) or textures (VDI/MT).
- Assembly: Guides, ejectors, waterlines, hot runner if applicable.
Step 3: Testing & Validation(Timeline: 1–2 weeks)
- T0/T1 trials: Establish process window; evaluate dimensions and cosmetics.
- Inspection: CMM, optical measurement; golden sample definition.
- Optimization: Gate tweaks, venting, cooling balance, steel-safe adjustments.
Step 4: Mass Production
- Stable runs: Repeatable temperatures, pressures, and timing.
- Quality control: FAI, in-process SPC, and final checks.
- Maintenance: Cleaning, lubrication, waterline descaling, and spares management.
Materials Used in Plastic Molds
Selecting the right mold steel and resin pairing drives lifespan, cycle time, and piece price—especially for glass-filled or corrosive materials.
Common Mold Materials
| Material | Properties | Applications | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| P20 Steel | Pre-hardened, versatile, economical | Medium-volume molds | $ |
| H13 Steel | High hardness, wear/heat resistant | High-volume, glass-filled resins | $$ |
| S136 Stainless | Corrosion resistant, high polish | Medical, food, transparent parts | $$$ |
| Aluminum | High conductivity, fast machining | Prototypes, short runs | $ |
Plastic Materials for Molding
- ABS: Tough and stable; excellent for cosmetic housings.
- Polypropylene (PP): Light and chemical resistant; packaging and appliances.
- Polyethylene (PE): Tough; common in blow-molded bottles and containers.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Clear and strong; optical and protective parts.
- Nylon (PA): Wear- and heat-resistant; gears and structural components.
Plastic Mold Cost Factors
The most frequent question that we usually get: what is the price of a plastic mold? These are the factors to use to construct an actual budget range.
Factors Affecting Mold Cost
Part Complexity Basic: $2 000-5000 Intermediate: $5 000-20 000 Advanced: $20 000-100 000 and above (e.g., mirror gloss, lifters/slides, micro features)
Mold Size Small less than 500 mm Medium between 500 and 1,000 mm Large more than 1,000 mm (larger tools are more complex to steel, machine and cool)
Volume Requirements Production. 200-1000 shots (prototype); 1000-10,000 (low production); 10,000-100,000 (high production) (hot runners and automation)
Material Selection Tool steel grade; treatments (nitriding, PVD, hard chrome, special needs (SPI optical polish, VDI/MT textures, corrosion control).
Cavity Number Single cavity; Multi-cavity (2-64); Family mold (good flow and shrink control) is necessary.
Tolerance Requirements Standard +-0.1 mm; Precision +-0.02 mm; Ultra-precision +-0.01 mm and environment controlled.
Cost-Saving Tips
- Early design optimization part design (DFM) to eliminate slides, hotspots and sinks.
- Make count of match cavity and ramp match schedule equal to actual requirement.
- Standard components and modular inserts can be used.
- Buy in bulk to cover the cost of tools.
- Cooperation with seasoned manufacturers to reduce trial times.
How to decide a plastic mold manufacturer
The appropriate partner establishes lead time, yield and overall cost of ownership. Screen by the criteria below.
Key Criteria to Evaluate:
- Experience & Expertise – Business years, industry specialization (auto/medical/electronics), case tolerances, case depth.
- Quality Certifications- ISO 9001; ISO 13485 (medical); IATF 16949 (automotive).
- Manufacturing Capabilities 5-axis CNC, EDM, CMM; max mold size/tonnage; precision and environmental control.
- Engineering Support- DFM, moldflow, prototyping, hot runner and automation integration.
- Communication/Service – Phase gates, fast after sales support, project management.
The questions to ask about your manufacturer of Mold.
How is your average lead time?
Do you provide DFM analysis?
Which quality control processes do you employ?
Are you able to deal with adjustments and fixes?
What is your warranty policy?
Do you offer tooling storage?
Are you able to offer material certifications?
What are your payment terms?
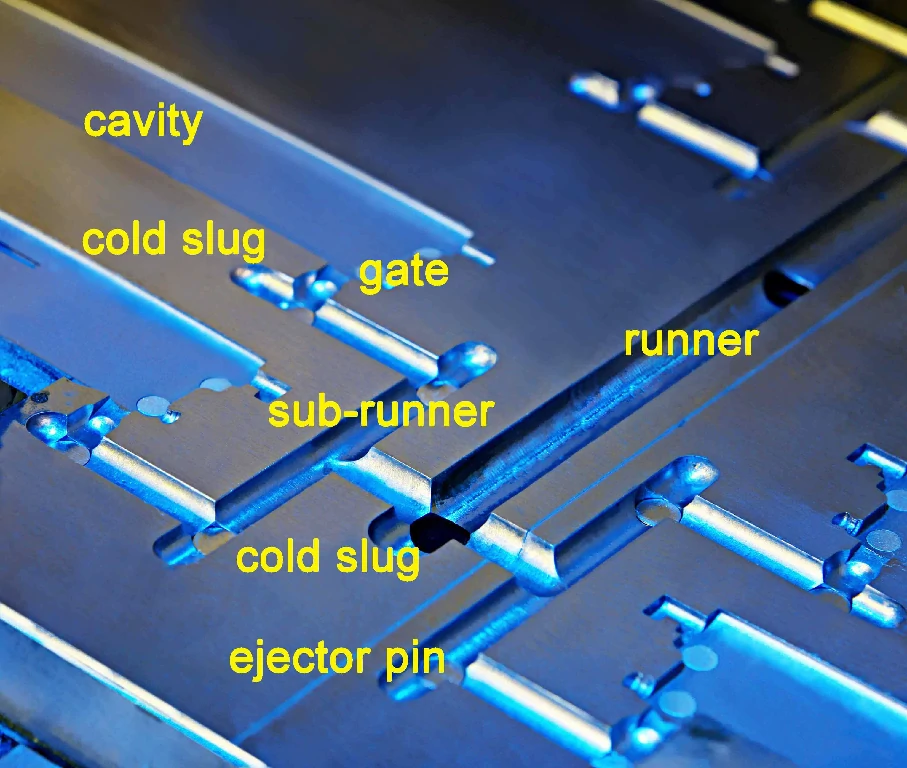
Quality Control in Mold Manufacturing
Quality is built in with precise measurement, documentation, and adherence to standards.
Inspection Methods
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
- Optical measurement and profilometry
- Surface finish testing (Ra, gloss)
- First Article Inspection (FAI), PPAP for automotive
Industry Standards
- ANSI/ASME, DIN, JIS dimensional and tolerance standards
- PPAP and APQP practices for automotive
- Device history records for medical
Common Challenges and Solutions
Most molding issues can be prevented with proactive design and process tuning. Here are frequent problems and fixes.
Warping and Surface Defects in Plastic Molding
| Issue | Problem Description | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warping Issues | Dimensional deformation affecting assembly. | Uneven walls, fiber orientation, unbalanced cooling, residual stress. | Uniform walls and ribbing; balanced cooling; adjust pack/hold and mold temp; select low-shrink or optimized GF content. |
| Flash/Burrs | Excess material along parting line. | Insufficient clamp force, worn parting surfaces, overpacking. | Increase clamp force; refit parting faces; tune injection pressures; gate optimization. |
| Short Shots | Incomplete filling. | Low melt temp, high runner resistance, poor venting. | Raise melt/mold temps; enlarge gate/runner; improve venting; consider higher-flow resin. |
| Sink Marks | Depressions in thick sections. | Localized shrinkage and insufficient packing. | Convert thick walls to ribs; increase pack pressure/time; add local cooling; move or resize gate. |
| Surface Defects | Splay, burn marks, flow lines, visible weld lines. | N/A | Improve drying and venting; reduce shear; apply appropriate texture; reroute flow with gate changes. |
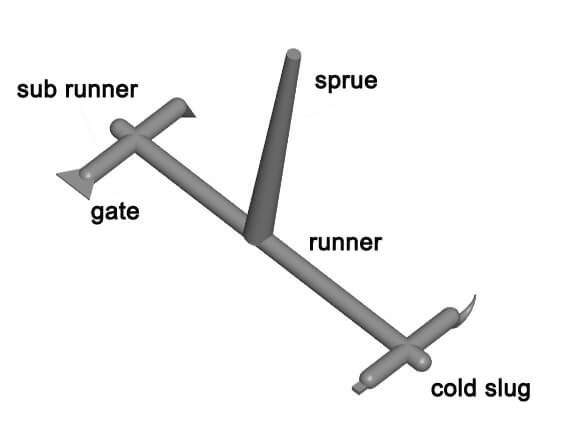
Plastic Mold Technology Trends in the Future
New capabilities are directly translating into reduced cycles, quality, and speedy launches.
- 3D Printing Integration
Allow additive manufacturing Rapid inserts and conformal cooling Rapid inserts and conformal cooling provide faster and evenly cooled parts and extreme cycle time reduction.
- Smart Molds (IoT Sensors)
Data-driven process would reduce the defects, quicker installations, and real-time process windows are embedded with temperature and pressure sensors.
- Sustainable Materials
Improved processable resin recyclable and bio-based with modular cores and replaceable inserts increase space, therefore, extending the life of the tool and waste reduction.
- Design Optimization based on AI
Parameters setting, defects prediction, and automatic gate/cooling with the help of AI reduce trial times, waste, and time-to-market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Top 10 essential questions about plastic molds
A plastic mold is a precision tool that is utilized in injection molding to make plastic parts from injection molding machine. It has two major sections: the cavity (which makes up the outside) and the core (which makes up the inside). When molten plastic is injected at high pressure, the plastic fills the space between these components,cools down,solidifies and releases from plastic mold in the desired part.
Molds are usually constructed from hardened steel or aluminum and they can be simple, single cavity systems or highly complex multi cavity systems that produce over 10 parts per cycle.
The injection molding process follows these key steps:
1. Clamping: The mold closes and is held together by injection molding machine
2. Injection: High pressure pushs molten plastic into mold cavity via runner and gate
3. Cooling: The heated plastic cools and solidifies inside the mold
4. Ejection: The mold opens and the finished part is ejected from the machine.
This cycle typically takes from 15 seconds to 2 minutes depending on part size and complexity.
P20 Steel: Pre-hardened steel ideal for medium-volume production (500,000-100,000 cycles). Good balance of cost and durability.
H13 Steel: Tool steel for high-volume production (200,000-500,000+ cycles). Excellent wear resistance and can be heat-treated.
S136 Steel: Stainless steel with good corrosion resistance for medical parts, transparent components, or corrosive resins.
Aluminum (7075, 6061): Used for prototype molds or low-volume production for quick machining and lower cost, but short lifespan.
The typical timeline is 6-10 weeks:
Weeks 1-2: Design phase including CAD modeling, DFM analysis, and moldflow simulation
Weeks 3-8: CNC machining, EDM (electrical discharge machining), polishing, and assembly
Weeks 9-10: Mold trials, testing, and optimization
Complex molds with multi-action slides, lifters, or hot runner systems may require 6-12 weeks. Parallel engineering (pre-ordering standard components) can reduce lead time by 10-20%.
Mold costs vary significantly based on complexity:
Simple single-cavity molds: $2,000 – $10,000
Medium complexity (2-4 cavities): $10,000 – $30,000
Complex multi-cavity molds: $30,000 – $100,000+
High-precision or family molds: $100,000 – $300,000+
Factors affecting cost include: cavity Qty, part size and complexity, tolerance, surface finish, mold material, hot vs cold runner, and production volume requirements.
Mold lifespan ranges from 50,000 to 1,000,000+ cycles depending on:
Mold material: Aluminum (50,000-100,000), P20 steel (100,000-500,000), H13 steel (500,000-1,000,000+)
Resin type: Abrasive materials like glass-filled nylon wear molds faster than standard plastics
Maintenance: Regular cleaning, lubrication, and preventive care significantly extend life
Operating conditions: Proper temperature control, injection pressure, and cooling management reduce wear
Single-cavity molds: Produce one part per cycle. Best for large parts or low-volume production.
Multi-cavity molds: Produce multiple identical parts per cycle. Ideal for high-volume production to reduce per-part cost.
Family molds: Produce different parts in one cycle. Useful when multiple components are needed together.
Hot runner molds: Use heated channels to keep plastic molten, eliminating waste and reducing cycle time.
Cold runner molds: Use unheated channels where plastic solidifies and must be removed. Lower initial cost but more material waste.
ABS: Strong, impact-resistant, good surface finish. Used in automotive, electronics, toys.
Polypropylene (PP): Chemical resistant, flexible, low cost. Used in containers, packaging, medical devices.
Polycarbonate (PC): Transparent, high impact strength. Used in lenses, safety equipment, electronics.
Nylon (PA): High strength, wear resistant. Used in gears, bearings, mechanical parts.
Polyethylene (PE): Flexible, chemical resistant. Used in bottles, films, containers.
Moldflow analysis is computer simulation that predicts how molten plastic will fill, pack, cool, and warp in the mold before any steel is cut. It identifies potential problems such as:
Short shots: Incomplete filling of the cavity
Weld lines: Weak points where flow fronts meet
Air traps: Trapped gases causing defects
Warpage: Part distortion during cooling
This analysis minimizes costly mold revisions, reduces trial-and-error, optimizes gate placement and cooling, and accelerates time-to-market by 20-40%.
Yes, common repairs and modifications include:
Parting line repair: Re-machining worn or damaged parting surfaces
Cavity welding and polishing: Filling scratches, dents, or worn areas
Ejector pin replacement: Replacing worn or broken ejection components
Adding material: Welding steel to reduce dimensions or fix errors
Removing material: Machining to increase part size or add features
Minor modifications cost $500-$3,000. Major changes like adding cavities or redesigning features can cost $5,000-$25,000 and may take 2-6 weeks.
Introduction to Your own Plastic Mold Project
You can use this guide to evaluate the plan for production, and it explained the fundamentals: mold architecture, process windows, steels and resin, cost drivers, and quality control.
DFM and moldflow have enabled our engineering team to deliver hundreds of tools to the automotive, medical, and electronics industries, and our team accomplished this by minimizing trial runs and ramp-up time and also due to their ability to achieve tight tolerances and cosmetic quality. Post your 3D files, resin, cosmetic class and volume of the target here,you will receive a transparent, line-item quote and feasibility consultation that will allow to start your business in a flash with confidence.
Ready to Start Your Mold Project?
- ✓ Free DFM Analysis
- ✓ Competitive Pricing
- ✓ Fast Turnaround
- ✓ ISO Certified Quality
Downloadable Resources
- Plastic Mold Steel Selection Guide(pdf)
- Cost Estimation Worksheet (Excel)
- Plastic mold manual(PDF)
- Plasttic Mould Maintenance Handbook(PDF)
Further Reading: Injection Mold Cost & Pricing Guide
Interested in learning more about the cost and pricing of injection molds? Explore our comprehensive resources below, including cost calculators, expert tips, and practical advice to help you manage your mold investment wisely.
Injection Mold Cost Smart Calculator
— Get an instant estimate for your mold cost with easy input.
What is the Cost of Injection Mold?
— Discover key factors that affect mold pricing.
How to Manage Costs When Buying Molds from China
— Practical tips for international buyers.
The Real Price Tag: Uncovering Hidden Costs in Chinese Injection Moulding
— Learn how to avoid unexpected expenses.
Mastering Injection Molding Costs: A Comprehensive Guide
— In-depth strategies and real-world case studies.
For more industry insights and helpful tools, visit our blog.
