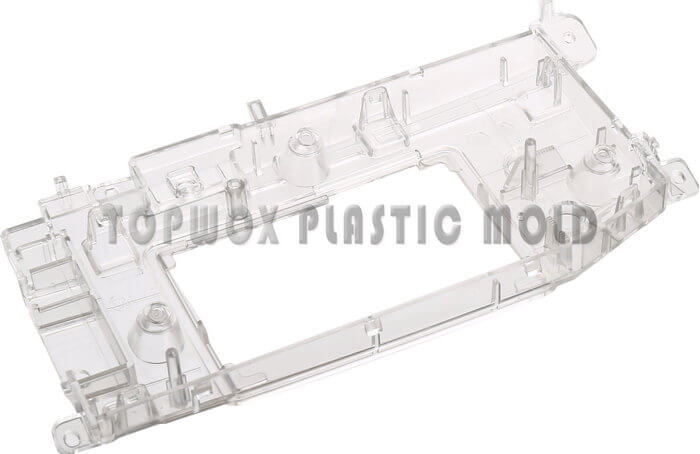
Polycarbonate injection molding
Topworks is a professional manufacturer of poly-carbonates injection molding.
We have more than 10 years of production experience in poly-carbonates injection molding
We have rich experience in producing extra wall thickness poly-carbonates and ABS/PC injection molding parts.
Our PC injection molding covers the following industries:
- Automobile parts
- Medical instruments
- Aerospace
- Packaging field
- Electronic appliance
- optical lens
- LED lighting
The maximum wall thickness of the PC product can reach 3 cm, but the surface does not shrink, and there are no bubbles inside.
- EXTRA WALL THICKNESS POLY-CARBONATE INJECTION MOLDING CASE
#1 CASE



2# CASE





What is Poly-carbonate injection molding?
Poly-carbonate resin is plastic with excellent performance, high transparency, good impact toughness, creep resistance, and a wide injection temperature range.
Process characteristics of PC: melt viscosity has little sensitivity to shear rate, but high sensitivity to temperature
It has no obvious melting point, the high viscosity of the melt, easy hydrolysis of resin at high temperature.
And PC injection is easy to get cracked.
To increase the fluidity of the melt, it is not necessary to increase the injection pressure but to increase the injection temperature.
It is required that the runner path and gate of the mold are short and thick to reduce the pressure loss of the melt, and at the same time with a higher injection pressure;
The resin needs to be sufficiently dried before the injection molding to control the water content below 0.02%;
In addition, the PC resin should be insulated during the processing to prevent re-absorption;
Not only is reasonable product design required, but also the molding process should be properly controlled, such as increasing the mold temperature and post-processing to reduce or eliminate internal stress.
It should adjust the process in time according to the different conditions of the product.

Process:
Drying of raw materials
Even in very low moisture, PC injection molding can cause hydrolysis, breakage, molecular weight reduction, and strength reduction.
Therefore, before the molding, it should strictly control the moisture content of the polycarbonate raw material to be below 0.02% to avoid a decrease in the mechanical strength or the bubbles and silver streaks on the surface.
PC is extremely sensitive to water, so it must be fully dried before injection to reduce its water content to below 0.02%.
[table id=15 /]Injection temperature
The Poly-carbonate injection temperature depends on the shape, size, and structure of the product.
Generally, the temperature is between 270 and 320 °C in the molding.
If the material temperature is too high, over 340 °C, the PC will decompose, the product’s color will become darker, and defects such as silver, dark stripes, black spots, and bubbles will appear on the surface.
At the same time, physical and mechanical properties are also dropped significantly.
PC is also sensitive to temperature; melt viscosity decreases with increasing temperature.
Barrel temperature is 250 ~ 320 ° C. (preferably not more than 350 ° C), and appropriate barrel temperature is good for PC plasticization.
If necessary, the internal stress should be removed by annealing.
The oven temperature is 125~135°C for 2 hours and naturally cooled to normal temperature.
Injection pressure
injection pressure greatly influences the physical and mechanical properties, internal stress, and molding shrinkage.
It has a great influence on the appearance and releases property of the products.
Too low or too high injection pressure will cause some defects in the products. The injection pressure is controlled between 80-120 MPa.
For thin-walled, long-flowing, complex-shaped products with small gates, the higher injection pressure is selected to overcome the melt flow resistance and fill the cavity in time. (145 MPa).
Due to the poor fluidity, high-pressure injection is required for poly-carbonate injection molding. Still, it is necessary to eliminate the large internal stress of the parts (which may cause cracking) later.
Holding pressure and time
The holding pressure and the holding time also greatly influence the internal stress of the PC product.
If the holding pressure is minimal, the product is difficult to fill and firm.
There are usually shrinkage marks on the surface and a vacuum blister inside.
And if the holding pressure is too large, large internal stress can easily be around the gate.
In processing, high temperature and low pressure work together to solve this problem.
The choice of holding time should be determined by the thickness of the product, the size of the gate, the temperature of the mold, etc.
Generally, the small and thin products do not require a long holding time.
On the contrary, the thick wall PC molding products should have a longer holding time.
The length of the holding time is determined by the gate sealing time.
Injection speed
There is no obvious influence on the performance of PC products.
A thin wall, small gate, or deep cylindrical object is generally injected at medium or slow speed, preferably multi-stage injection:slow-fast-slow.
Mold temperature
Mold temperature control: 85~120 °C, generally at 80-100 °C.
For complex shapes, thin-wall Poly-carbonate part injection molding, the temperature can increase to 100-120 ° C, but it can not exceed the distortion temperature.
The mold wall temperature could be high to reduce the temperature difference between the mold wall and the PC material part, reducing the internal stress.
Screw speed and backpressure
Due to the high viscosity of PC melt, it is beneficial to plasticize and help good venting.
The rotation speed of the screw should not be too high.
Generally, it is suitable for 30-60r/min.
The backpressure control is preferably between 10-15% of the injection pressure.
Additives
PC injection molding should strictly control the use of release agents in the process, and the use of recycled materials should not exceed three times, and the usage should be below 20%.
Mold requirements
1) Design the runner as big and short as possible.
For less pressure loss, plastic mold adopts circular cross-section runners.
And runners need grinding to reduce the flow resistance of the melt.
2) The injection gate can be of any type, but the cooling water channel diameter is not less than 15mm.
Injection machine requirements
The maximum injection volume (including runners, gates, etc.) of the product is required to be no more than 70-80% of the nominal injection volume;
Clamping pressure: 0.47 to 0.78 tons per square centimeter of finished product projected area (or 3 to 5 tons per square inch);
Machine size: The weight of the finished product is about 40 to 60% of the capacity of 1 shot.
If the machine is expressed in polystyrene (Aussie), it needs to be reduced by more than 10%.
Screw: The length of the screw should be at least 15 times of diameter, and the L/D is 20:1. The compression ratio is preferably from 1.5:1 to 30:1.
The stop valve at the front end of the screw should adopt a sliding ring type.
Why silver streaks and how to prevent poly-carbonate injection molding?
Silver streaks refer to the streaks formed by the moisture of plastic in a cylinder due to the material particles are not sufficiently dried before molding.
Or the sufficiently dried material particles stay in the hopper for too long, and the hopper is WITHOUT effective insulation measure, lead to re-absorb the moisture. The water content exceeds the specified requirements again.
The moisture in particles is vaporized under the high temperature in the cylinder, which causes the resin to degrade during the melting process.
The Co2 accumulates inside the molten resin, and when filling, it flows into the cavity with the Poly-carbonate to form silver streaks.
As a result, the strength of the plastic part is significantly reduced to becomes brittle. This type of silver streak often occurs and relatively easy to identify.
It is usually distributed more evenly along the flow direction and is densely found on the entire surface of the plastic part sometimes.
The fundamental solution for eliminating these silver streaks is to dry the pellets fully, and the moisture of the pellets must be controlled by less than 0.03%.
For this reason, it must strictly control the process conditions for drying the raw materials, and also it should measure the water content of the pellets before molding.
Tips
In poly-carbonate injection molding production, a simple inspection method can be used.
Use two small glasses, and one detected pellet is sandwiched between the two glasses and then placed on a 280-300 degree heating plate.
When the pellet is gradually melted by heat, and after smooth pressurization to crush the melt, observe whether there are bubbles in the material; if there is no bubble, it is dried to be used for the next step; otherwise, it needs to continue drying.
If the silver streaks are caused by moisture absorption in the hopper, the heat preservation device should be set or improved in the hopper.
And it needs to control the amount of one feed so as not to cause the dry pellets to stay in the hopper for too long and absorb moisture again.
In general, the maximum residence time should not exceed 30 to 60 minutes.
Most of the hopper’s heating and heat preservation devices are provided with infrared bulbs on the upper part of the hopper.
Generally, the heating power of 25 to 30 W is required per square meter of area.
Decompose reason
The decomposition of the silver streaks refers to the super-heating decomposition of the resin during the molding to generate a gas such as carbon dioxide producing silver streaks on the surface of the plastic part.
There are many specific reasons for the thermal decomposition of the melt :
- the temperature of the barrel is too high;
- dead space in the barrel or nozzle;
- the residence time of the melt in the barrel is too long;
- the molecular weight of the resin has been reduced. Therefore, the impact strength of the plastic part is inevitably lowered, the texture becomes brittle, and the function cannot be met.
This type of silver streaks is generally recognizable from the appearance, and its distribution on the surface of the plastic part has no regularity,
In addition, the appearance of decomposed silver streaks is often accompanied by the darkening of the plastic parts or even the appearance of brown spots, which is especially evident in the hot runner, which can be used for discriminating the decomposition of silver streaks.
For the decomposition of silver streaks, workers should take the corresponding measures according to the reasons for decomposition.
- If the high temperature of the barrel causes it, the temperature of the section should be lowered;
- if there is a dead angle in the barrel or nozzle, the dead part should be cleaned, and the dead angle should be removed;
- if it is due to the melt residence time in the cylinder too long, the molding cycle should be shortened as much as possible.
It should be considered to replace the injection molding machine with a smaller capacity for processing if it still failed.
Structure reason
This kind of silver streak is due to the mixing air in the mold cavity with molten material due to the unreasonable structural design of plastic parts, severe uneven wall thickness, or sudden cross-section change.
They cause the molten material to expand or contract rapidly during mold filling.
This kind of default mainly affects the appearance but with little influence on plastic parts’ strength and impact toughness.
The structural silver streak is characterized in that when the process conditions are fixed, the shape and position of the silver wire are also fixed.
The silver wire is generally found along the injection direction, and the positions where the silver streaks occur are mostly behind the abrupt cross change sections.
Because the sudden change of cross-section causes the structural silver streaks and serious uneven wall thickness; as a result, the surface of the plastic parts often has faults such as depression and shrinkage and sometimes even generates bubbles inside the plastic parts somewhat.
Changing the injection speed can generally eliminate structural silver streaks. When the cross-section of the plastic part changes little, the injection speed can be slowed down.
When the injection speed is SLOW, the flow material can be smoothly filled into the mold cavity so that the flow material cannot be mixed with air when passing through those sections, and silver streaks can be avoided.
However, a short shot may occur when the injection speed is too slow, which needs to be solved by adjusting other process conditions such as mold temperature and nozzle temperature.
When the cross-section varies greatly, the injection can adopt a higher speed and increase the injection pressure so that the gas can be forcibly discharged from the parting surface.
If the silver streaks cannot be eliminated by improving the injection speed or increasing the injection pressure, improving the plastic part structure and the mold venting system may work.
Sprue and runner reason
The silver streaks due to the runner are caused by the unreasonable design of the gating system or partial blockage.
The causes and solutions :
(1) Too large sprue draft. If the sprue draft is too large, the flow material will leave the sprue wall at the initial stage of injection, which would result in gaps.
As the mold cavity is gradually filled, air will be mixed and trapped in the flow material to enter the mold cavity to form silver streaks.
The main feature of the silver streaks is that their distribution is completely along the injection direction.
To eliminate the streaks, it should eliminate the possibility of resin decomposition by injecting it into the air first and checking whether the sprue is appropriate.
If the angle is over 1 0 degrees, the above may occur.
An angle of 4~6 degrees is appropriate.
If the angle is too small, demoulding will be difficult, and material flow will be hard.
These silver streaks are sometimes eliminated by changing the injection speed, but the fundamental method is to trim or replace the sprue to reduce the cone angle.
(2) The unreasonable gate design. If the cross-sectional area of the gate is too small, turbulence will occur when the flow passes through the gate, which will mix the melt with air to generate silver streaks near the gate.
This kind of streaks is mainly characterized by radial distribution along the injection direction with the gate as the center.
The elimination is to enlarge the gate or change the cross-sectional shape of the gate to eliminate the silver streaks.
If the injection speed is appropriately reduced while reworking the gate, it will be more effective.
(3) The cold material at the nozzle causes the blockage of the gating system during the injection process.
The blockage of the runner or gate is similar to that of silver wire produced by too small a gate.
When identifying such silver wire, traces of cold material should be found in the injection system.
The solution is to increase the material temperature in the mold and increase the nozzle temperature.
Venting reason
This kind of silver streak is when we cannot expel air from the PC flow material during the mold filling process.
The main feature is that obvious weld lines accompany it, and silver streaks often appear near the weld lines, while there are no silver streaks in other parts.
The basic method to eliminate this kind of silver streaks is to change the gate position, cut effective exhaust slots or modify the plastic part’s main structure.
In actual injection molding production or mold testing, changing the injection molding machine set is often a good way to adjust injection pressure and injection speed, change a temperature difference between fixed mold and moving mold, etc.