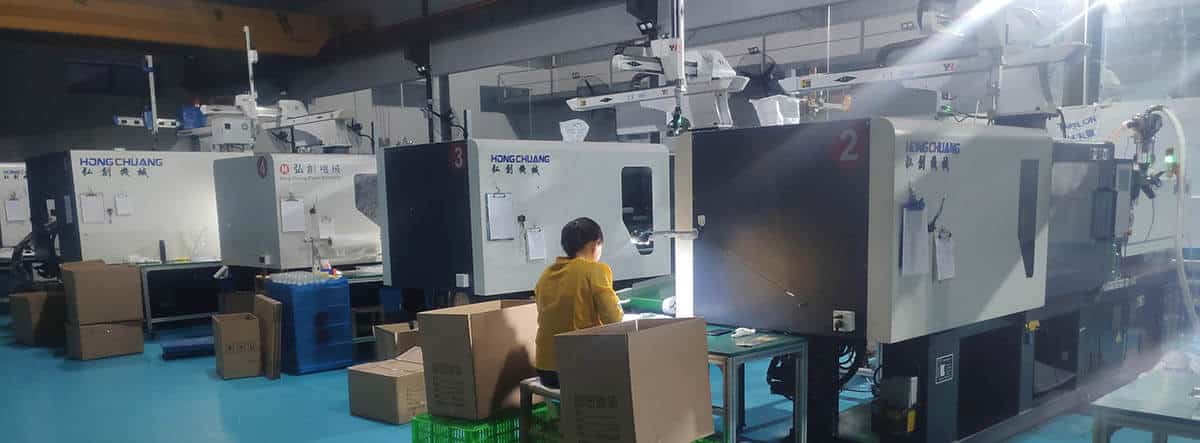
Consumer Electronics and Injection Molding: Fusion of Innovation
Injection molding transforms the consumer electronics experience. This high-volume manufacturing process shapes the slim, seamless designs and tough, resilient casings that define modern devices.
Table of Contents
As electronics evolve, injection molding innovations keep pace. Intricate molds churn out the sophisticated parts needed to embed new capabilities. China’s vast manufacturing capacity propels each generation of must-have gadgets.
Let’s examine the critical role of injection molding in consumer electronics and what the future holds for even more exciting products.
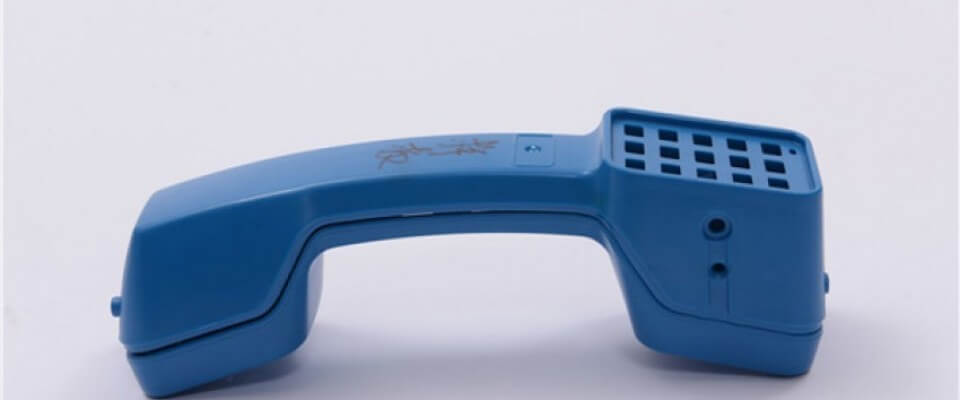
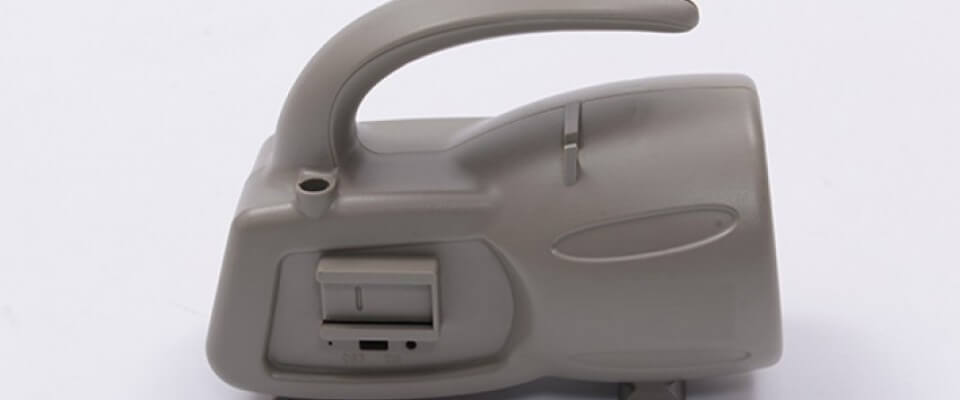
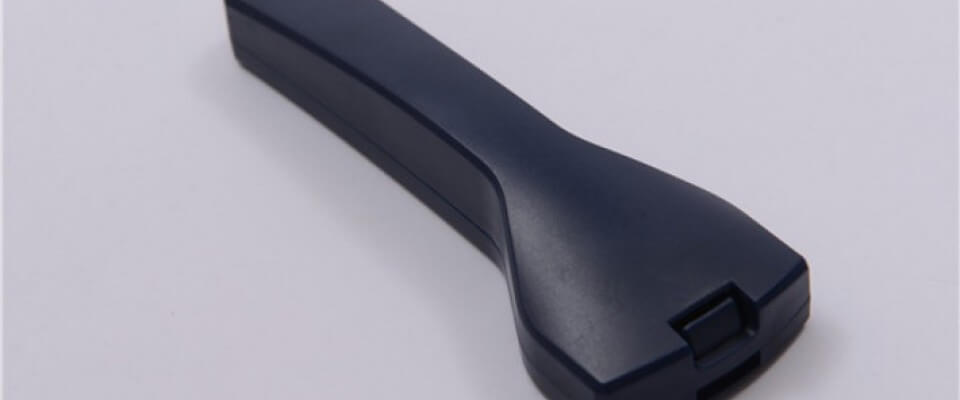





How Injection Molding Revolutionized Electronics
Early electronics depended on sheet metal boxes and hand assembly. But the rise of polymers and automation opened new possibilities.
Injection molding offered an efficient, economical way to package electronics. Melted plastic could encapsulate innards in durable, lightweight shells.
With molded parts, electronics companies found creative freedom limited only by what molds could produce. New designs emerged:
- Sleeker, thinner, more sculpted exteriors
- Molded-in features like grips, buttons and lenses
- Snap-fit assemblies replacing fasteners
- Colors, textures, and surface details
This manufacturing fusion empowered innovation in form and function. It unlocked the visual refinement and tactile quality that defines premium electronics today.
Role of Injection Molding in Consumer Electronics
Injection molding touches nearly every consumer electronic device produced today. Applications include:
Device Housings
Seamless enclosures protect interior components while enabling curvaceous designs. Multi-shot molding combines hard and soft-touch polymers.
Components and Attachments
Buttons, knobs, sockets, clips and other functional parts integrate into the housing mold. Insert molding adds metal or plastic inserts.
Screen and Lens Covers
Clear plastic cover windows safeguard displays and cameras. Light pipes and diffusers enhance visibility.
Insulating Cases
Foam molding makes rigid, impact-resistant carrying cases lined with insulating foam.
Connectors and Cables
Multi-shot molding combines flexible insulation and rigid fittings in a single part. Overmolding coats connectors and cables.
Heat Sinks and Shielding
Heat dissipating and radiation blocking enclosures leverage thermally conductive resins.
Decorative Finishing
Pad and laser printing, plating, painting and other methods add decorative finishes.
Branding
Molded-in logos, patterns and styling features help define brand identity.
Injection molding fuses electronics functionality with exterior aesthetics for a seamless user experience. Production automation drives costs down even as devices gain new capabilities.
Materials and Process Innovations
Specialized materials and processing methods expand the design possibilities for consumer electronics:
- Multi-shot molding combines rigid and soft-touch polymers for grippy control surfaces and decorative trims.
- Metal/plastic hybrids enable chrome, steel and alloy finishes like Apple’s iPhone stainless steel band.
- Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) makes flexible, stretchy molds for soft-feel covers.
- In-mold decoration applies graphics as part of the molding process for a seamless decorated surface.
- Micro-texturing imparts matte finishes that resist fingerprints and glare.
- Nano-molding forms microscopic surface structures measured in nanometers, similar to a moth’s eye, reducing reflectivity.
- Antimicrobial additives in plastics inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, especially important for wearables.
Key applications in consumer electronics include:
Enclosures – Laptop chassis, TV and monitor casings, router housings, etc. Integrated parts consolidate components.
Buttons and keypads – Molding makes raised buttons and rubbery keypads with customized symbols and textures.
Connectors and ports – USB, HDMI, and custom connectors fuse strength, flexibility and precision.
Lenses and light pipes – Injection molded optical parts direct LED light for displays and indicators.
Gaskets and seals – Molded rubbery materials prevent dust and moisture from entering sensitive electronics.
Mounts and fasteners – Integrated snaps, hinges, and clips simplify assembly and access. Screw bosses provide mounting points.
Insulators and spacers – Electrical and thermal isolation of circuits and components prevents shorts.
Electronics Manufacturing in China
Electronics assembly offers a path from poverty to middle class for millions of Chinese workers. Injection molding powers production:
- Shenzhen is the heartland of electronics, with Foxconn and other giants driving innovation.
- Pearl River Delta cities form a thriving tech hub centered on Guangzhou.
- Yangtze River Delta is also vital – Shanghai and Suzhou host advanced IT firms.
- Inland cities with lower costs, like Chengdu, Chongqing and Wuhan, continue to grow.
This vast workforce allows the quick ramp-up needed for new product launches. China’s supply chain provides the specialty resins and advanced molding capabilities consumer brands demand.
With its unique mix of molded parts production, assembly infrastructure and skilled workers, China shapes each generation of electronics hitting the global market.
Injection Molding Role in New Technologies
Injection molding will remain crucial as consumer electronics continue evolving with new capabilities:
Flexible and foldable devices depend on specialized materials and processes to bend screens. Plastic substrates will likely supplement or replace glass.
Stretchable electronics can bend, twist and deform well beyond today’s flexible devices. Liquid silicone molds embed wavy circuit traces in elastic polymers.
Additive manufacturing will enable more complex plastic parts, but injection molding will remain ideal for mass production. Expect hybrid molds with 3D printed inserts.
Sustainable materials like bioplastics from renewable resources provide an eco-friendly alternative to oil-based resins. Recycled plastics also play a bigger role.
Smart surfaces such as touch sensors, heating/cooling elements and displays integrate seamlessly via injection molded electronics.
Metal and ceramic replacement will shift more structural parts to tougher, lighter injection molded plastics.
Invisible seam integration hides all traces of fasteners, gaps and transitions for a perfect unified design.
Injection molding offers the efficiency and adaptability essential to keep consumer electronics exciting and widely accessible. Expect even tighter fusion between industrial design and manufacturing as molds bring new ideas to life.
The Next Wave of Portable Electronics
Many future product concepts rely on innovations in materials, miniaturization and seamless design integration that injection molding makes possible:
- Thinner smart phones with edge-to-edge flexible displays
- Full-surface interactive control panels
- Novel foldable, rollable and sliding form factors
- Ultra-lightweight frames and structural components
- High-density batteries and circuits integrated into housing
- Low-profile or hidden connectors and ports
- Conformal antennas and sensors molded into exterior
- Transparent or translucent casings with embedded lights
- Nanostructured metal/plastic hybrid materials
Molding provides a path to commercialization that’s affordable at scale. As electronics keep getting smarter, more connected and intuitive to use, injection molding will fuse together the inner workings and outer appeal that consummates the user experience.
The consumer electronics revolution has only just begun. Injection molding will play an integral role as each new product pushes the limits of aesthetics and functionality. Emerging technologies hold the promise of portables beyond our imagination today. But advanced molding capabilities will turn those ideas into tomorrow’s must-have devices.
